Ammonium permanganate, a violet-brown crystalline solid, represents a significant industrial chemical with applications in organic synthesis and specialized oxidation processes. However, its utility is counterbalanced by severe hazards, including explosive reactivity, acute toxicity, and environmental risks. This report synthesizes critical safety protocols, hazard mitigation strategies, and Safety Data Sheet (SDS) management practices essential for handling this compound. Key findings emphasize the necessity of explosion-proof infrastructure, rigorous contamination controls, and comprehensive SDS systems to prevent catastrophic incidents.
Understanding Ammonium Permanganate: Essential Safety Measures for Handling and Use
Handling chemicals carefully can mean the difference between safety and danger. Ammonium permanganate is a strong oxidizer used in many industries. However, unsafe handling can lead to fires, burns, or environmental harm. Knowing how to use this chemical properly is essential for everyone working with it. In this article, you’ll discover what ammonium permanganate is and the safety steps you need to follow.
Ammonium Permanganate: A Brief Overview
-
Chemical Composition and Properties
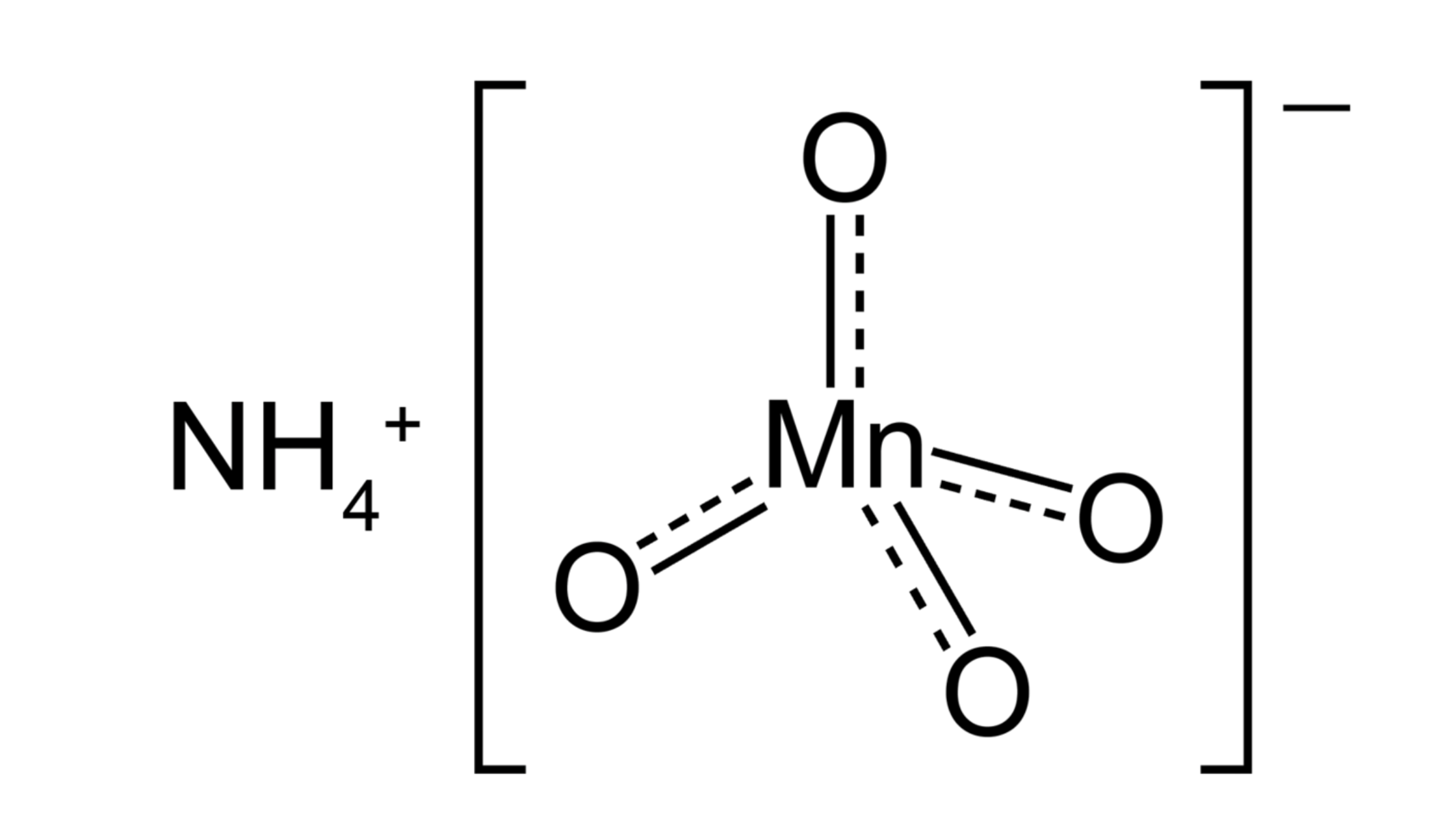
Ammonium permanganate is a chemical compound made of ammonium ions and permanganate ions. It appears as dark purple or reddish-brown crystals. When dry, it looks solid and stable, but it can easily become reactive if mishandled. It dissolves slightly in water, forming a deep purple solution. Its stability makes it useful but also means it should be stored properly to prevent accidents.
-
Common Uses and Applications
You’ll find ammonium permanganate in water treatment plants because it effectively destroys bacteria and contaminants. It’s also used in chemical processes to create other compounds or as an analytical reagent in labs. Some industries use it to clean equipment or test samples. Its powerful oxidizing ability makes it suitable for these tasks but requires careful handling.
-
Why Safety Is Critical
Despite its usefulness, ammonium permanganate is dangerous if mishandled. Data shows that oxidizing agents are involved in many chemical accidents each year. Injuries can happen quickly through burns, toxic exposure, or environmental damage. Protecting yourself and the environment should always be your top priority when working with this chemical.
Essential Safety Measures When Handling Ammonium Permanganate
-
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Always wear safety gear. Use chemical-resistant gloves to prevent skin contact. Goggles protect eyes if splashes happen. A lab coat or apron keeps your clothing safe. Masks or respirators are necessary when working with dust or fumes. Choose gear rated for chemical hazards.
-
Storage Guidelines
Store ammonium permanganate in cool, dry places away from direct sunlight. Keep it in airtight, corrosion-resistant containers. Separate it from acids, organic materials, and other incompatible chemicals. Label containers clearly to avoid mix-ups. Good storage reduces risk of accidents.
-
Handling Procedures
When moving or mixing, do so carefully. Use non-reactive tools and containers. Avoid creating dust or splashes. Work on a stable surface with secondary containment—think of it as a spill guard. Never handle it near heat sources or open flames.
-
Emergency Response Protocols
In case of a spill, contain it immediately. Use absorbent materials designed for chemicals and dispose of waste properly. For skin contact, wash with plenty of water and remove contaminated clothing. If it enters your eyes, rinse for at least 15 minutes. Call emergency services if exposure occurs.
Regulatory and Safety Standards
-
International and Local Regulations
Agencies like OSHA and EPA set rules for handling hazardous chemicals. These include documenting storage and use, labeling containers, and training employees. Always stay informed about local safety laws and standards for chemical use.
-
Safe Laboratory and Industrial Practices
Before working with ammonium permanganate, do a risk assessment. Ensure your team is trained in its hazards and safety procedures. Conduct regular safety audits to prevent accidents. Keeping safety protocols current helps everyone stay protected.
-
Labeling and Warning Signs
Proper labels on containers inform everyone about the contents and hazards. Use clear warning signs in storage areas. This prevents accidental mishandling and reminds staff to follow safety rules.
Tips for Safe Disposal and Waste Management
-
Disposal Regulations
Dispose of ammonium permanganate waste according to local laws. Don’t pour it down the drain unless approved. Contact licensed chemical disposal services for guidance. Proper disposal prevents pollution and legal issues.
-
Recycling and Reuse Options
When possible, recycle unused chemicals or find ways to reuse them. This reduces waste and environmental impact. If disposal is necessary, neutralize leftover chemicals with appropriate agents first.
-
Preventing Environmental Contamination
Stop spills from spreading with barriers or absorbent materials. Use neutralizers, like sodium bisulfite, to deactivate residual oxidizers. Proper disposal of neutralized waste keeps water and soil safe.
How to Keep Ammonium Permanganate Safe with SDS Management
Handling ammonium permanganate safely is crucial, especially in industrial plants and laboratories. This chemical is powerful, but it can cause accidents if not managed correctly. Safety Data Sheets (SDS) are your best tool for understanding and controlling risks. Proper SDS management can prevent injuries and ensure compliance with regulations. This article will show you how to keep ammonium permanganate safe by making the most of SDS practices.
-
Chemical Properties and Uses
Ammonium permanganate is a bright purple solid with strong oxidizing properties. It’s used in water treatment, disinfection, and chemical analysis. Because of its strong oxidizing nature, it can react violently with many substances.
-
Associated Risks and Hazards
This chemical can cause fires, explosions, and burns. Its oxidizing power means it can easily ignite combustible materials. It’s toxic and can irritate the skin and eyes. If it leaks, it harms the environment — especially aquatic life.
-
Legal and Regulatory Requirements
Agencies like OSHA and EPA set rules for handling ammonium permanganate. These laws aim to protect workers and the environment. Companies must follow proper storage, handling, and disposal rules to stay compliant.
The Role of SDS in Chemical Safety Management
✅What is an SDS and Why Is It Critical?
An SDS provides vital info about chemicals. It lists hazards, handling steps, protective gear, and emergency procedures. With this info, workers can understand risks and act safely.
✅Mandatory SDS Documentation and Accessibility
Regulations require keeping current SDS for every chemical. They must be easy for staff to access anytime. Storage cabinets, digital libraries, or clear labels help achieve this.
✅Interpreting and Using SDS Effectively
Key sections for ammonium permanganate include hazard identification, first aid measures, handling and storage, and emergency response. Training staff to read and understand these parts ensures safe work practices.
Developing a Comprehensive SDS Management System
-
Establishing a Centralized Document Control System
Keep all SDS in one place—digitally or physically. Digital systems make updates simple and quick. Always track versions to avoid outdated info.
-
Employee Training and Safety Protocols
Run regular training sessions on SDS interpretation. Teach staff how to follow protocols and use protective gear. Follow SOPs that include SDS info to guide daily tasks.
-
Integrating SDS into Emergency Preparedness
Use SDS to prepare for spills, fires, or exposures. Develop clear plans that include specific steps from SDS sections. Practice drills that emphasize understanding of hazard info.
Best Practices for Safe Handling and Storage Guided by SDS
-
Proper Handling Techniques
Always wear PPE—gloves, goggles, and aprons—as advised by SDS. Use proper transfer tools and avoid pouring too quickly, which can cause splashes.
-
Storage Conditions and Segregation
Store ammonium permanganate in cool, ventilated areas. Keep it away from powders, acids, and flammable materials. Use secondary containment to prevent leaks.
-
Transportation and Disposal
Transport in labeled, sealed containers. Follow SDS and regulations to prevent accidents. Dispose of waste according to SDS directions or local laws, avoiding environmental contamination.
Monitoring, Review, and Continuous Improvement
-
Regular Safety Audits and Inspections
Check that SDS is available, current, and understood. Inspect storage areas for hazards or damage. Fix issues before accidents happen.
-
Updating SDS and Safety Procedures
Update SDS when suppliers release new versions or regulations change. Review safety protocols annually and after any incident.
-
Leveraging Technology for SDS Management
Use software to organize, update, and share SDS quickly. Mobile apps allow workers to access safety info on the spot, reducing mistakes.
Conclusion
Ammonium permanganate’s dual role as an industrial reagent and high-risk oxidizer demands multilayered safety infrastructures. Institutionalizing engineering controls, PPE mandates, and SDS rigor reduce incident probabilities, while emergency preparedness limits collateral damage during failures. Future research should prioritize chronic exposure studies and greener alternatives to mitigate reliance on this hazardous compound. Regulatory bodies must enforce cross-industry compliance, leveraging lessons from past oxidizer disasters to prevent recurrence.

Leave A Comment